Food Safe 3D Printer Filament: From Compliance to Customization
3D printing has become a cornerstone of agile manufacturing — enabling custom, cost-effective, and on-demand part production. But in industries like food and beverage, the adoption of additive manufacturing has been slower compared to sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and medical device manufacturing, which embraced 3D printing early on for prototyping and increasingly for end-use parts.
Why? One major blocker: The lack of certified food safe 3D printer filament.
Manufacturers in this space operate under strict safety regulations, especially for parts that either come into contact with or are in close proximity to food and beverage. As a result, there's a growing need for printed materials that aren’t just strong and precise — but also certified, cleanable, and capable of withstanding sanitation protocols. Fortunately, new materials are now being certified under existing food safety standards, opening new possibilities for use in food and beverage production.
This post is a guide for food and beverage manufacturers exploring 3D printing: What to look for in food safe 3D printer filament, where it fits on the factory floor, and how to apply it effectively.
Why Food Safe 3D Printing Materials Matter
For factory teams in the food and beverage industry, speed and adaptability are essential. 3D printing supports those goals by enabling:
- Rapid creation of custom tooling
- Quick turnaround on replacement parts
- Minimal downtime for production lines
But not just any filament will do.
In food environments, even parts that never touch food directly may require materials that meet food-contact standards. This includes conveyor guides, pushers, diverters, chutes, and machine components near product lines.
Until recently, most 3D printing materials simply didn’t meet those safety requirements. In fact, many of these materials hadn’t even been tested to see if they met food-contact standards. That left manufacturers relying on more expensive machined plastics or metals — slowing down the very efficiency that industrial 3D printers are meant to deliver.
Where Food Safe 3D Filament Fits in Manufacturing
To understand how food safe 3D printer filament fits into the manufacturing process, it's helpful to use the industry-standard “zone” concept:
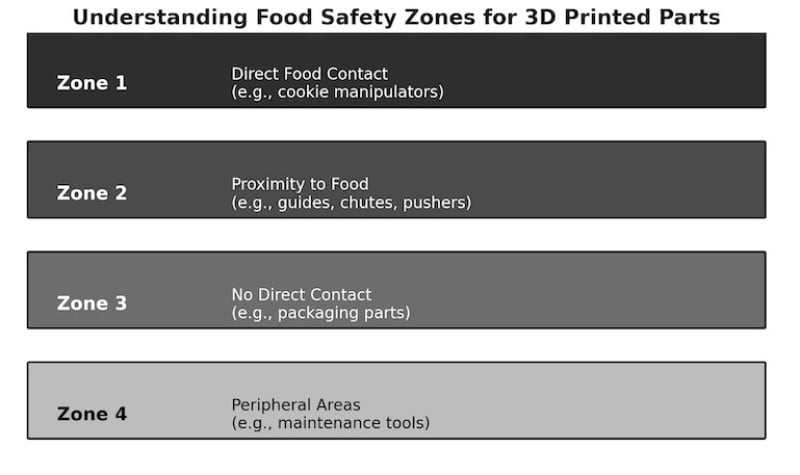
- Zone 1 – Direct food contact (e.g., cookie manipulator arms)
- Zone 2 – Proximity to food (e.g., guides, funnels, pushers)
- Zone 3 and 4 – No contact, but still subject to hygiene standards (e.g., packaging lines)
Food safe filament is most transformative in Zones 1 and 2. In these areas, compliance with certifications like NSF/ANSI Standard 51 and FDA CFR Title 21 is often a requirement — not a recommendation.
What to Look for in a Food Safe 3D Printing Filament
Not all filaments are created equal. Here's what makes a material suitable for food-contact use in industrial settings:
| Requirement | Why It Matters |
| NSF/ANSI 51 or FDA-compliant (US) | Ensures the material won’t leach chemicals or alter food |
| EC 1935/2004 (Europe & Asia) | Prevents material contamination that could trigger costly recalls, health risks, and brand damage |
| Smooth, cleanable surface | Reduces microbial growth risk |
| Durability | Withstands harsh cleaning, wear, and repeated use |
| Moisture and heat resistance | Maintains integrity in factory conditions |
| Non-abrasive | Prevents damage to machinery and delicate products |
| Certifications for specific food types | Some filaments may exclude use with alcohol, etc. |
It's important to note that certification typically applies to the filament material only, not the final printed part. Factors like print geometry, surface finish, and cleaning protocols all influence final food safety.
Real-World Applications for Food Safe 3D Printer Filament
Food safe 3D printer filaments can be used in a wide range of applications, especially for tooling and MRO (maintenance, repair, operations):
- Pushers and diverters on conveyor systems
- End-of-arm tooling in robotic pick-and-place operations
- Funnels and chutes guiding raw or packaged goods
- Packaging support tools used during filling or sealing
- Non-marring clamps and brackets that secure sensitive components
The true value lies in flexibility—these parts can be customized to a specific machine or product (e.g. A different bottle shape for a new bottled water product), adjusted on the fly, and replaced without long lead times.
Real-World Example: Controllogic's Cookie Manipulator
Controllogic, a manufacturer specializing in custom tooling for the food and beverage industry, needed a solution that could meet both performance demands and food-contact safety standards. Traditional materials limited their ability to rapidly prototype and produce parts for use on food production lines.
By switching to Nylon White FS, a filament certified by NSF to NSF/ANSI Standard 51 and compliant with FDA CFR Title 21, they were able to design and 3D print a cookie manipulator that could be deployed directly into food-handling environments.
The result? A 65% increase in addressable applications for their existing 3D printer. The new material allowed Controllogic to unlock new use cases that were previously off-limits due to food safety concerns.
Nylon White FS provided the cleanable, non-abrasive, and durable properties needed for the application, while ensuring compliance with stringent regulatory standards.
This case highlights why food-contact certified filament like Nylon White FS is more than a material — it’s a strategic enabler for innovation in food and beverage manufacturing.
Food Safe Filament Options: How Do They Compare?
Here’s a look at how some common materials stack up in terms of safety, performance, and usability for 3d printing in food industry applications:
| Material | Food Safe Certified? | Pros | Cons |
| PLA | Sometimes (depends on additives) | Easy to print, biodegradable | Low strength and heat resistance |
| PETG | Often (FDA-compliant grades) | Chemical resistance, stronger than PLA | May require post-processing to reduce porosity |
| Standard Nylon | Rarely certified | Strong, durable | Usually not food-contact approved |
| Nylon White FS | Certified by NSF to NSF/ANSI Standard 51, FDA CFR Title 21 | Smooth, durable, chemically resistant, suitable for factory environments | Certified for all food contact types except alcohol |
When choosing a food safe filament, don’t just look at its chemical makeup — also consider your post-processing capabilities, operating environment, and internal compliance protocols. Nylon White FS stands out as a rare material that is both industrial-grade and food-contact certified, making it an ideal choice for factory applications.
Making Printed Parts Truly Food Ready
A certified filament is a start, but here are best practices to make sure your parts are production-ready:
- Avoid crevices and tight corners that trap food particles
- Favor sloped surfaces for better drainage and cleanability
- Post-process when needed (e.g., sanding or vapor smoothing) to reduce roughness
- Use certified print beds and nozzles, or dedicate a printer solely for food-contact parts
- Validate cleaning and sanitation protocols specific to your production line
Remember: Just because a filament is certified doesn’t mean printed parts will automatically pass food safety audits.
The Big Opportunity: Why Food Safe 3D Printer Filament is a Game-Changer
Manufacturers in the food and beverage space face some of the toughest compliance requirements in the industrial world. For any part that touches or even comes close to food, the material used must be proven safe — not just in terms of composition, but in how it's processed, cleaned, and maintained.
Traditionally, this has meant turning to machined plastics like Delrin or even stainless steel — both of which are expensive, slow to produce, and restrict design flexibility.
Nylon White FS breaks that barrier.
With a material that is certified by NSF for food contact and compliant with FDA CFR Title 21, the door is open for a wide range of applications that were previously off-limits to additive manufacturing. This not only removes blockers in early-stage operational conversations, but fundamentally changes what's possible on the factory floor
A Strategic Shift for Factory Teams
For manufacturers looking to reduce downtime, simplify tooling, and improve responsiveness, food safe 3D filament isn’t a novelty—it’s a strategic enabler.
It allows:
- Faster line changeovers
- Reduced inventory needs
- Rapid turnaround on tooling
- Greater flexibility in design and iteration
And with certified options now on the market, it’s possible to gain these efficiencies without compromising safety.
Ready to Explore Certified Food Safe Filament?
If your team is exploring how to bring additive manufacturing into regulated environments like food and beverage production, certified food-contact materials offer a powerful new option.
Talk to an expert to explore how Nylon White FS can modernize your factory floor.
Never miss an article
Subscribe to get new Markforged content in your inbox
